Understanding the : A Key Player in Your Body's Health and Function
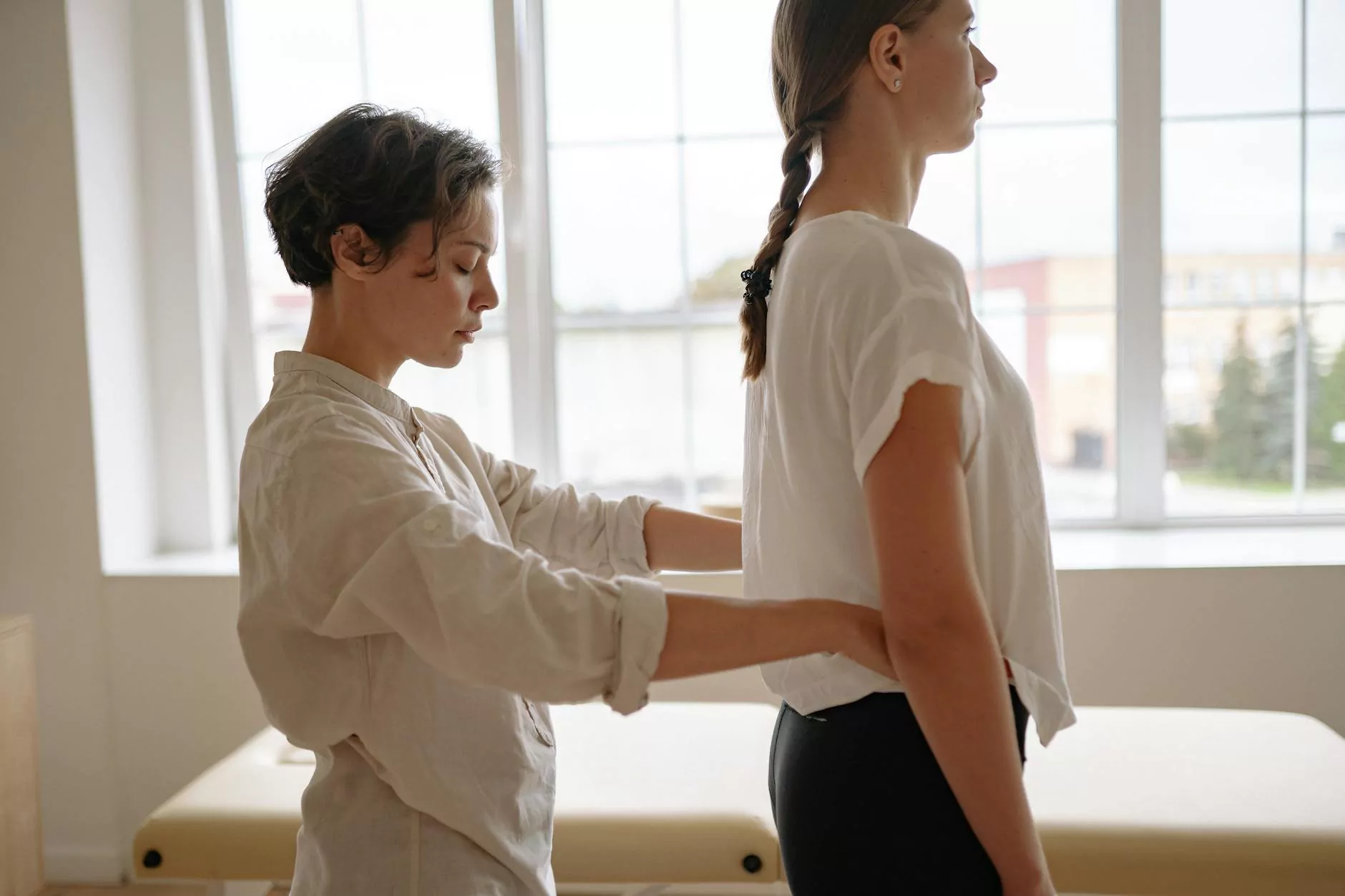

In the realm of health, medicine, and chiropractic care, understanding the complex network of nerves and their roles is crucial for diagnosing and managing various conditions. Among these vital nerves, the stands out due to its profound influence on both local and systemic health. This comprehensive guide delves into what the is, how it operates within the human body, its significance in medical treatments, especially in chiropractic care, and how education plays a pivotal role in promoting awareness and optimal health management.
What Is the ?
The is a specific spinal nerve rooted at the fourth thoracic vertebra (T4) level. As a part of the thoracic spinal nerve segment, it originates from the thoracic spine, which is the middle segment of the vertebral column, consisting of 12 vertebrae (T1-T12). The primary functions of the include transmitting sensory information from parts of the torso and back, as well as motor signals to muscles within its distribution area.
Location and Anatomy of the
The exits the spinal cord through the intervertebral foramen between the T4 and T5 vertebrae. It then branches into dorsal and ventral rami:
- Dorsal ramus: Supplies sensation and motor innervation to the muscles and skin of the back.
- Ventral ramus: Extends to anterior and lateral parts of the body, supplying intercostal muscles, skin, and other tissues of the thoracic wall.
This nerve plays a critical role in the sensory and motor functions related to the thoracic region, impacting posture, respiration, and the nervous supply to vital organs.
The Significance of the in Health & Medical Care
The influences numerous physiological processes. Its health and proper functioning are essential for maintaining the integrity of thoracic and upper abdominal structures. Disruptions or damages to the can lead to a spectrum of health issues, ranging from localized pain to systemic symptoms affecting organ function.
Common Conditions Associated with Dysfunction
While the is relatively protected within the thoracic spine, certain circumstances can impair its function:
- Herniated or Bulging Disc: The intervertebral disc affecting T4 can impinge on the nerve root, resulting in pain or neurological deficits.
- Thoracic Spine Injuries: Trauma or fractures in the T4 vertebra can impact nerve signaling.
- Muscle Spasms: Tension in surrounding muscles can compress or irritate the nerve.
- Postural Issues: Chronic poor posture can alter spinal alignment, affecting nerve health.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Age-related degeneration may put pressure on the nerve roots.
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Issues
Proper diagnosis of related problems involves a combination of clinical assessments, imaging studies, and neurological evaluations:
- Physical Examination: Includes palpation, range of motion tests, and neurological assessments.
- Imaging Techniques: MRI scans provide detailed images of the spinal cord, vertebrae, and soft tissues, helping identify nerve impingements or structural anomalies.
- Nerve Conduction Studies: Measure how well electrical signals pass along the nerve pathways.
Understanding the precise nature and location of nerve impairment guides effective treatment strategies.
Effective Treatments for Dysfunction
Treatment options vary based on the severity and cause of the issue. They encompass conservative approaches, advanced medical interventions, and alternative therapies:
Chiropractic Care and the
Chiropractic professionals are experts in treating spinal nerve issues, particularly those related to misalignments and subluxations. Specific chiropractic techniques focus on restoring alignment and alleviating pressure on the :
- Spinal Adjustments: Gentle, precise manipulations aimed at correcting vertebral misalignments and reducing nerve impingements.
- Soft Tissue Therapy: Massage and myofascial release to relax surrounding muscles, decreasing nerve irritation.
- Postural Rehabilitation: Education on ergonomics to prevent future nerve compression.
The goal is to enhance nervous system function, reduce pain, and restore optimal biomechanical function.
Medical Interventions and Advanced Treatments
In cases where conservative care is insufficient, medical options may include:
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants.
- Injections: Nerve blocks or epidural steroid injections to reduce inflammation and nerve irritation.
- Surgical Options: In severe cases, procedures such as decompression or spinal fusion may be necessary to relieve nerve compression.
Educational Role in Managing Issues
Education is a cornerstone in preventing and managing problems. Patients, healthcare providers, and students in health sciences must understand the importance of spinal health, proper posture, ergonomics, and early intervention.
Institutions like iaom-us.com play an essential role by providing comprehensive resources, training programs, and educational materials on the anatomy of the , diagnostic techniques, and treatment modalities.
The Interconnection of with Overall Health and Well-Being
The doesn't operate in isolation; it is part of an intricate network that impacts multiple body systems:
- Respiratory Function: Innervation of intercostal muscles influences breathing efficiency.
- Digestive System: Nerve signals affecting the upper abdominal organs.
- Circulatory Health: Proper nerve function supports healthy blood flow and cardiovascular health.
- Postural and Musculoskeletal Integrity: The T4 level contributes to spinal stability and overall posture.
Innovations in Diagnosing and Treating
The field of health sciences is continually advancing, including the diagnosis and treatment of nerve-related issues:
- High-Resolution Imaging: 3D MRI and functional imaging techniques provide better visualization of nerve and spinal cord health.
- Neuro-modulation Therapies: New approaches like transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) offer pain relief and nerve repair support.
- Regenerative Medicine: Stem cell research and biological therapies aim to promote nerve repair and regeneration.
Expertise in Managing Disorders at IAOM-US
At iaom-us.com, specialized in Health & Medical, Education, and Chiropractors, experts are committed to advancing knowledge about the and offering innovative, evidence-based solutions. Their programs emphasize:
- Comprehensive education for practitioners and students about spinal nerves and their systemic roles.
- Advanced chiropractic techniques tailored to address specific nerve impingements, including the .
- Patient-centered care focused on holistic health, prevention, and long-term wellness strategies.
The Future of Research and Therapy
As technology and medical understanding evolve, future directions include personalized medicine approaches that adapt treatments based on genetic, structural, and functional profiles. Integration of digital health, AI diagnostics, and minimally invasive procedures promises to revolutionize how we manage nerve-related health issues, including those involving the .
Conclusion: Prioritizing Nerve Health for a Better Quality of Life
Understanding the and its vital role within the nervous system underscores the importance of early detection, proper management, and ongoing education. Innovative chiropractic interventions, combined with medical advancements and comprehensive learning, pave the way for enhanced health outcomes and improved quality of life. Whether you are a healthcare provider, student, or patient, recognizing the significance of the can make a profound difference in your health journey.
For those seeking expert guidance and up-to-date resources on health, iaom-us.com offers invaluable support, training, and expert services dedicated to advancing understanding and treatment of nerve-related health issues.
t4 nerve